When several issues of debt securities (bonds and note) are outstanding, a hierarchy can be specified:
- Secured – The status of the claims of bondholders backed by specific assets of the issuer to secure the payment of interest and the repayment of the principal to the extent of the value of the creditors’ security interest in the assets serving as collateral.
- Senior unsecured – The status of the claims of bondholders on the earnings and assets of the issuer only after satisfaction of the claims of any secured bondholders and other secured creditors and to the extent of the value of the collateral securing the secured creditors’ claims – represents the general creditor status;
- Senior subordinated – The status of the claims of the debenture holders to the interest and principal payments of the issuer that are subordinated to the claims of the secured and the unsecured, unsubordinated general creditors but before the claims of all other creditors of the issuer;
- Subordinated – The status of the claims of creditors on the earnings and assets of the issuer that are satisfied only after secured, unsubordinated and senior subordinated debt but before the claims of junior subordinated debt; and
- Junior subordinated – The status of the claims of creditors on the interest and principal payments of the issuer that are satisfied after the claims of all other creditors but before the claims of all classes of equity, it being subordinated to all other classes of debt in the event of the issuer’s liquidation.
| Subordination of Mezzanine Debt |
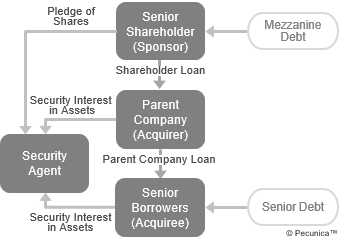 Source:
|


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.