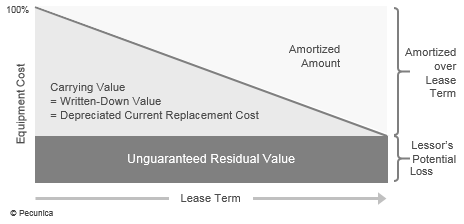
The value of a limited-life asset’s is reduced as a result of the passage of time or its use in the production of goods and services by means of amortization. A leased asset’s amortization depends on the asset’s historical cost, estimated economic life, residual value and the amortization method chosen. Most finance leases are amortized on the basis of constant payments over the lease term and structured according to the individual requirements of the lessee.
| Lease Amortization |
 Source:
|
Different terms are used for the amortization of different classes of noncurrent assets. The term used for the periodic allocation of the cost of a tangible asset (other than land and natural resources) over its estimated useful economic life is depreciation, both for accounting purposes (accounting depreciation) and tax purposes (tax depreciation). Depletion is the term used for the exhaustion of a natural resource, such as mineral deposits, standing timber or oil through mining, cutting, pumping or other extraction as well as for the way in which the cost of the natural resource is allocated. The term “amortization” is commonly used only to refer to the periodic allocation of the cost of a financial asset or an intangible asset, such as goodwill or a patent, over its economic useful life. While a lease is "amortized" as a financial asset of the lessor, it is "depreciated" as a fixed asset by the lessee.
| Asset Amortization Methods | |
|---|---|
| Type of Asset | Method |
| Property, Plant & Equipment (Fixed Asset) | Depreciation |
| Natural Resources | Depletion |
| Financial Assets | Amortization |
| Intangible Assets | Amortization |
Both US GAAP and IFRS lease accounting exclude licensing agreements for items such as motion picture films, plays, manuscripts, patents and copyrights (intangible assets) and rights to explore for or exploit (deplete) natural resources and applies only to tangible fixed assets (property, plant and equipment). Therefore, finance leases are considered depreciated by lessees – not amortized or depleted. However, as financial assets, they are considered amortized by the lessor.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.