Gregory Autin | July 1, 2024
The subsidiarity principle states that the responsibility should, as far as possible, be assumed by the smallest "responsible" unit, with higher-level units intervening only when the lower units cannot.
To take effective legal action to protect communities, it is necessary to determine the extent to which the various levels and structures of government can be held responsible and accountable for environmental protection. Most environmental problems have a local dimension and local authorities are the level of government closest to the citizens, which indicates that this is the responsibility of local authorities.
Generally, local authorities are responsible for taking the necessary measures to protect the environment and combat climate change and have the power to take the appropriate action. In some countries, the law may place responsibility for achieving environmental targets on local authorities, so that they have both the powers and a positive obligation to act – a duty of care.
A municipality should also be able to decide the local services it deems necessary or reasonable to promptly and effectively deal with the challenges. Such public services should be allocated to local authorities since they can generally perform that responsibility better than regional or state agencies.
Because of the significance of localizing the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), the right of local authorities to participate in environmental decision-making must be strengthened by acknowledging this. The right to participate in the affairs of a local authority empowers local governments to react to environmental issues arising in their communities, in line with the subsidiarity principle.
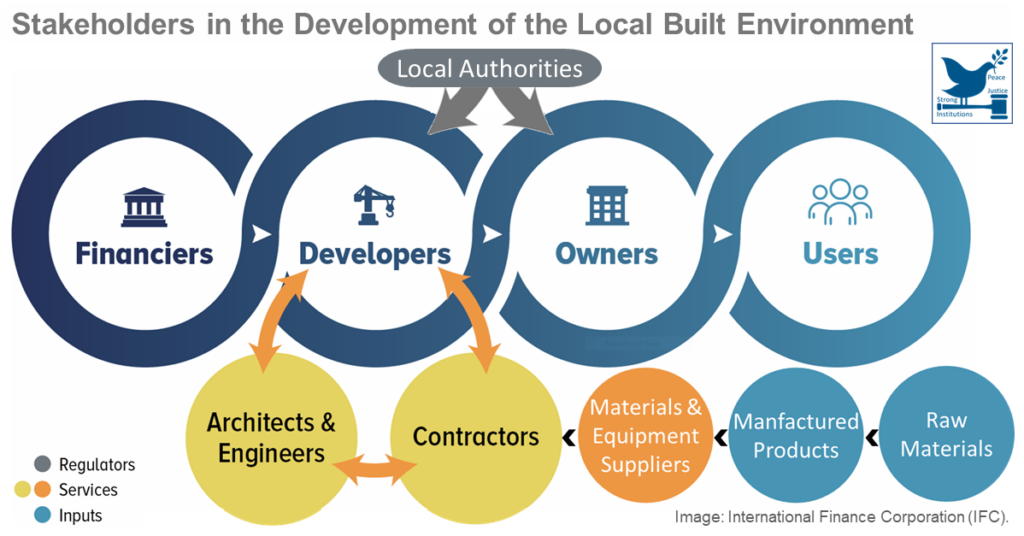
For the development of an eco-friendly built environment, national, regional and local regulations promote “green building”. This suggests application and compliance with relevant SDGs to include prioritizing building renovation over new-builds; appropriate conservation, renovation and use/re-use of our urban cultural heritage; and applying requirements for sustainable design and construction and promoting high-quality architecture and building technologies.