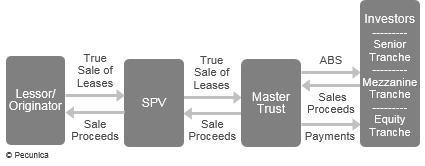
A master trust is an investment structure that allows for the holding and management of a portfolio of assets and a dynamic collateral profile allowing for the addition of new collateral from the originator in order to support prefunding or future funding. For securitization, master leases are held in a master trust to facilitate the issuance of asset-backed securities (ABSs). Master trust securitization structures use a master indenture and series supplements to secure the different tranches (series of notes) issued under the master indenture. Since securitization rewards economies of scale, many lessors use automated underwriting and credit scoring systems that allow for a greater volume of lease receivables by ABS originators. The participation interest structure commonly makes use of master trusts.
| The Master Trust Flow Process |
 Source:
|
Synthetic leases are commonly used for high-volume small-ticket equipment via a master lease and through the use of a special purpose vehicle (SPV). The SPV is usually owned by the lessee/operating company and given just enough independence such that it is not consolidated with the operating company on its balance sheet. The leases are recorded as assets on the balance sheet of the SPV, which allows the SPV to take advantage of the tax benefits of ownership, while the equipment is leased to the operating company under an operating lease for accounting purposes, allowing the lessee to recognize the lease payments as expense.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.