Financial statement analysis is essential in order to gain an understanding of the historical, current and potential profitability of a company. It is also critical in assessing the relative stability of revenues and earnings of the company, its levels of operating and financial risk as well as the performance of management.
| The Financial Statement Analysis Process |
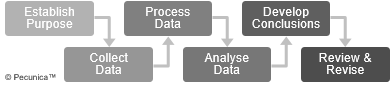 Source:
|
Comparative analysis is the measurement and comparison of variables in financial statements over two or more reporting periods or of two or more companies for the purpose of identifying operating results and competitive positions. The financial statements contain the variables that define the operating, investing and financing activities of the companies. Horizontal analysis and vertical analysis are two of the analytical techniques used for comparative analysis.
Vertical Analysis → % of Line Item to a Reference Item in a Given Period
Horizontal Analysis → % of Line Item Relative to Itself over Periods


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.