- International Accounting Standards, originally issued before 2004;
- International Financial Reporting Standards, issued as of 2004;
- SIC Interpretations, issued before 2002;
- IFRIC Interpretations, issued as of 2004; and
- Other pronouncements.
| IFRS Organization Structure |
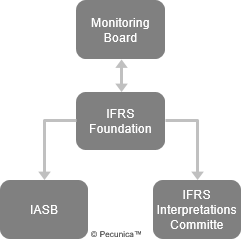 Source:
|
The IASB system requires of reporting entities the following financial statements and information:
- A statement of financial position (balance sheet) at the end of the period.
- An income statement and other comprehensive income for the period;
- A statement of changes in equity for the period;
- A statement of cash flows for the period;
- Notes summarizing the reporting entity’s accounting policies and other explanatory notes; and
- A statement of financial position of at the beginning of the earliest comparative period when a firm retrospectively applies an accounting policy or restates or reclassifies items in its financial statements.
Titles for the statements other than those above may also be used.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.