Unlike best-effort arrangements or club deals, arrangers must transfer all or part of their interest in the financing for the underwritten facilities to be syndicated to new lenders. Original lenders sell their loans to reduce their exposure to the industry or borrower or due to other business with borrower not materializing. Such liquidity enhances the attractiveness of the facilities to potential underwriters, which reduces the costs of funding to the borrower.
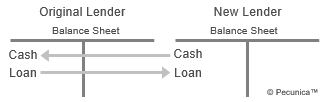
A loan sale is the sale of a loan’s cash streams to a third party without recourse, guarantee, insurance or other credit enhancement. It transfers ownership and control rights from the seller to the buyer of the loan, with the amount sold transferred from the seller’s to the buyer’s balance sheet.
A loan sale is a true sale, which is the outright, irrevocable nonrecourse transfer of the loan from the seller to the buyer. Loan sales are one of the principal means used by banks in order to comply with lending limits, meet capital-adequacy requirements and to decrease their credit risk, allowing banks to reduce single-name and industry credit risk concentrations within their credit portfolio.
| Loan Sale Impact on Balance Sheets |
 Source:
|
Depending on the jurisdiction, loan sales may be transacted by means of novation, assignment or participation. Under both US and English law, loans sales by either novation or assignment transfers loans from the seller’s to the buyer’s balance sheet. Where participations are considered as loan sales in the US, they are treated as lending to the loan originator and grantor in the UK.


Leave A Comment
You must be logged in to post a comment.