Sustainability performance targets (SPTs) are ESG metrics used to identify borrowers that adopt sustainability principles. Most loan documentation specifies certain SPTs for borrower compliance with general lending requirements.
Green loan principles (GLP) provide a standard for borrowers to apply in business operations with the objective of improving their sustainability performance, complying with environmental regulations, or ensuring long-term financial and operational stability. Green loan principles are based on green bond principles (GBPs), which are voluntary guidelines for the issuance of bonds that promote transparency, disclosure and reporting in the green bond market.
Green loans and green bonds aim to facilitate corporate social responsibility and sustainable financing and investing. Their proceeds are solely used to finance or refinance new and existing "green projects".
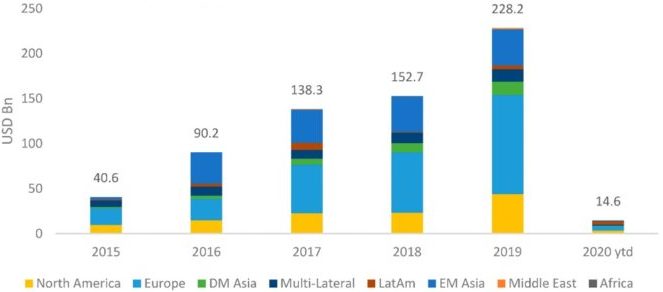

Sustainability linked loans (SLLs) promote sustainable development by inducing borrowers to achieve certain ambitious sustainable performance targets. By directly linking a loan's financial terms to sustainable performance targets, borrowers are encouraged to improve their sustainable development management.
Sustainability linked loan principles (SLLPs) set a standard for determining how financing can facilitate positive corporate performance by achieving measurable growth in financing for sustainable development – however, not restricted to green purposes. SLLPs are based on the borrower's (1) overall corporate social responsibility (CSR) strategy; (2) sustainability performance targets (SPTs); (3) reporting on their SPT achievement; and (4) sustainability performance verified by independent external review.
Besides the risk of greenwashing, there are several challenges to the wide use of green loans and bonds for company financing. The obstacles include the lack of harmonized global standards, perceived higher costs, the lack of product supply, and the infancy of the market.

