A mortgage is a lien on property to secure a borrower’s performance under the terms and conditions of the mortgage loan agreement. A mortgage provides the mortgage holder a legal mechanism to forecloseon the financing if the mortgage borrower defaults on the loan.
The provider of a mortgage loan is the mortgagee, to whom a lien on real property is assigned as security for the loan. The borrower of a mortgage loan is the mortgagor, who assigns to the mortgage lender a property lien on real estate the borrower owns as security for the loan. A real estate mortgage involves a mortgage note and a mortgage deed.
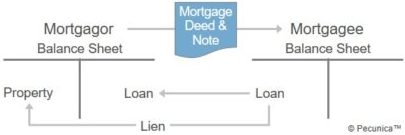
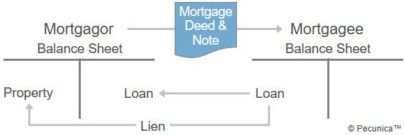
A mortgage note is a promissory note secured by a real estate mortgage evidencing the obligation of the mortgagor to repay to the mortgage holder the mortgage loan plus interest at a specified rate and over a specified period. The document that imposes the lien on the title to real property as security for a loan is a mortgage deed.
A mortgage is perfected by recording the mortgage deed in the local public land records. This allows the secured party to foreclose on the financing if the mortgagor fails to repay the loan or to otherwise perform as contractually required in the mortgage loan agreement.
Mortgages are conventionally used to finance the real estate that serves as the collateral to secure the loan (i.e., real estate mortgages). Chattel mortgages are used to secure the financing of tangible personal property (), such as equipment, fixtures, and the renovation of property.

