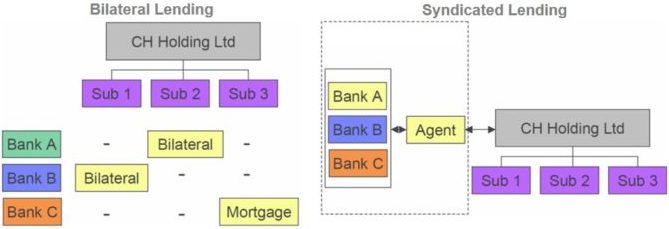

A syndicated facility is financing in which a revolving credit and/or term loan facility is arranged and provided through direct syndication and/or by more than one lender on uniform terms and conditions using common documentation. Syndicated loans are administered by a common party – usually the loan originator and lead arranger.
When the amount of financing required by a borrower is too large for a relationship bank to provide on its own, a club deal may be arranged. In a club deal, a group of banks underwrites the full amount of a loan at the outset of the transaction with no sub-underwriting or intention to subsequently reduce their investment in the loan ("final hold"). The club deal syndicate is closed when the facility agreements are executed (signed), without general syndication and without subsequently trading the loan in the secondary market.
Syndicated real estate lending finances newproperty investment/acquisition, the refinancing of existing facilities, property development as well as unsecured real estate lending and distressed refinancing. Commercial and investment banks account for the majority of the participation in syndicated real estate financing, followed by private equity and debt funds, insurers and pension funds, and building societies.
Funds are prevalent in the leveraged loan, real estate and infrastructure debt markets. Hedge funds, CLO/CDO and distressed debt funds provide mezzanine debt and subordinated debt in acquisition and real estate development and investment transactions frequently as loan-to-own investments. Alternative credit investors, such as direct lending funds, provide debt in the mid-market.

