Sustainable construction spans the value chain of development projects – siting, design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation and deconstruction. It considers a building's complete life cycle and focuses on the reduction of resource consumption, reusing resources, protecting nature, eliminating toxins, life-cycle costs, and product quality.
Sustainable procurement (SP) aims to reduce the consumption of goods within a building or premises and/or the sourcing of sustainable materials and equipment in order to minimize its negative impact on the community, society and the environment. Procurement is sustainable when developers make procurement decisions for projects that integrate requirements, specifications and criteria that protect the environment, are in favor of social progress, and support economic development.
Sustainable construction utilizes industrial waste, by-products or recycled materials to decrease carbon dioxide emissions and preserve natural resources. It seeks resource efficiency, improves the quality of products and services, and ultimately optimizes costs.
Whole-life costing encourages and recognizes sustainable development reporting, commissioning and certification initiatives that ensure all building services operate to their full potential. If materials are truly sustainable, their embodied energy – the amount of energy to produce it – and the operational energy is relatively low.
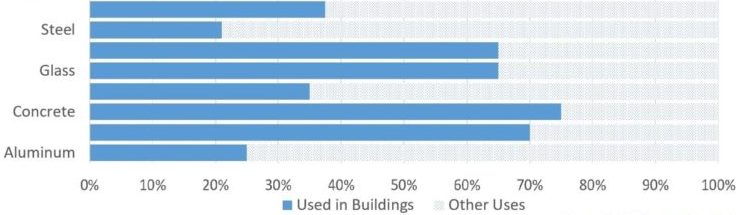

Sustainable construction depends in large measure on project procurement. Sustainable procurement practices may be imposed by legislation, the terms of the construction contract, or the policies of the developer. It is the responsibility of the developer to ensure that sustainable construction and sustainable procurement principles are adopted and implemented in their development projects.

